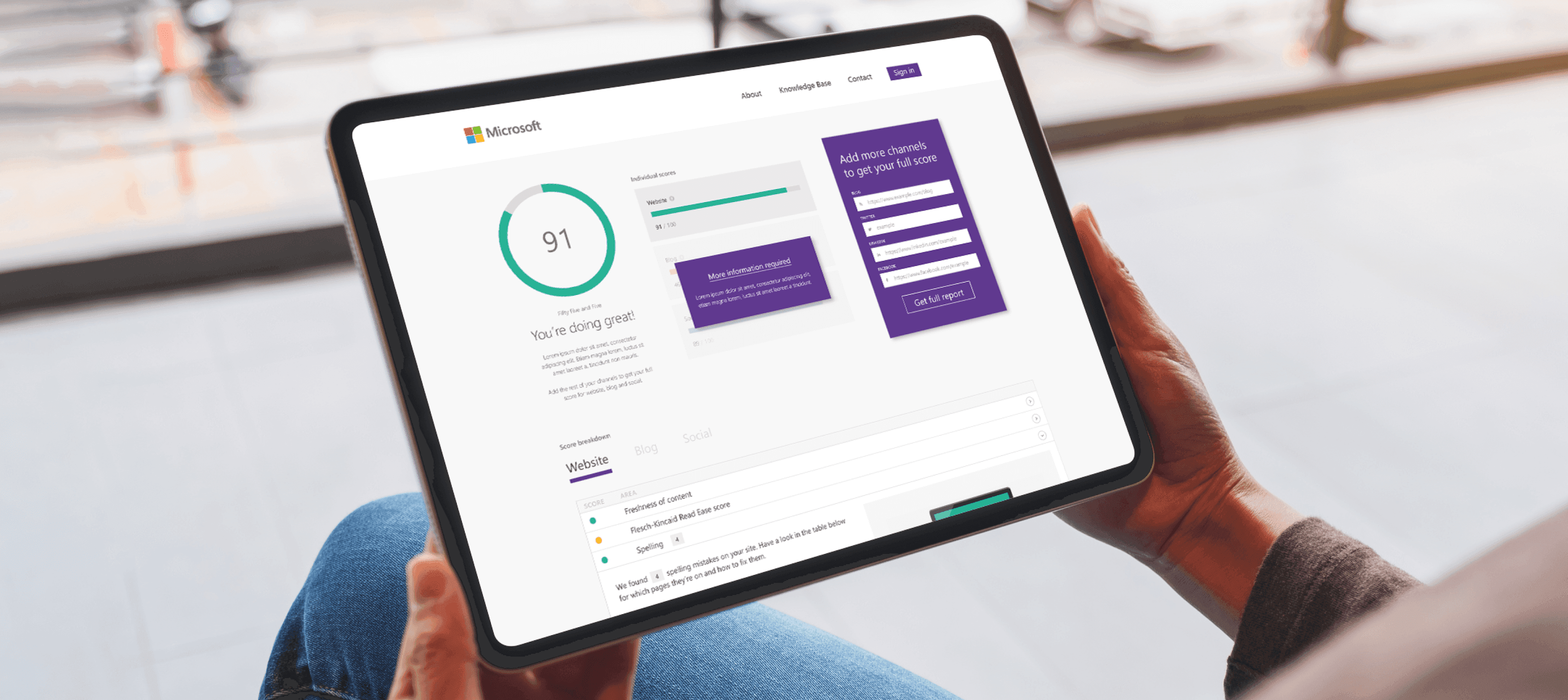
Drive Growth.
Drive Growth.
Drive Growth.
Drive Growth.
Drive Growth.
Win Customers.
Win Customers.
Win Customers.
Win Customers.
Win Customers.
Win Customers.
We deliver innovative marketing services, expert consultancy and advanced AI tools that empower B2B enterprise marketing teams.
We deliver innovative marketing services, expert consultancy and advanced AI tools that empower B2B enterprise marketing teams.
We deliver innovative marketing services, expert consultancy and advanced AI tools that empower B2B enterprise marketing teams.
Our services
Our services
Our services
We aim to revolutionise the world of B2B marketing agencies by leveraging AI to deliver innovative marketing services, expert consultancy and cutting-edge AI tools.
We aim to revolutionise the world of B2B marketing agencies by leveraging AI to deliver innovative marketing services, expert consultancy and cutting-edge AI tools.
We aim to revolutionise the world of B2B marketing agencies by leveraging AI to deliver innovative marketing services, expert consultancy and cutting-edge AI tools.
We aim to revolutionise the world of B2B marketing agencies by leveraging AI to deliver innovative marketing services, expert consultancy and cutting-edge AI tools.
We drive results for B2B enterprise
We drive results for B2B enterprise
Here's what our clients have to say
Here's what our clients have to say

Read our 2025 AI Influencers report
Read our 2025 AI Influencers report
Read our 2025 AI Influencers report
This exclusive guide is customised specifically to you and your painpoints. Want to know how we did it? And how you can use our techniques in your marketing? Request access and we'll share the whole thing for free.









Download our report for personalised (by AI of course) advice in this new era.
Download our report for personalised (by AI of course) advice in this new era.
Download our report for personalised (by AI of course) advice in this new era.
For a personalised report please use your work email address.
I would spend fifty five minutes defining the problem, and then I would need just five minutes to solve it.
The Leather Market
Weston Street
London, UK
SE1 3ER
+44 20 3743 7897
© Fifty Five and Five 2025 - Our head office is registered in England and Wales as company no. 07508740. VAT no. 107280831. Privacy policy.
I would spend fifty five minutes defining the problem, and then I would need just five minutes to solve it.
The Leather Market
Weston Street
London, UK
SE1 3ER
+44 20 3743 7897
© Fifty Five and Five 2025 - Our head office is registered in England and Wales as company no. 07508740. VAT no. 107280831. Privacy policy.
I would spend fifty five minutes defining the problem, and then I would need just five minutes to solve it.
The Leather Market
Weston Street
London, UK
SE1 3ER
+44 20 3743 7897
© Fifty Five and Five 2025 - Our head office is registered in England and Wales as company no. 07508740. VAT no. 107280831. Privacy policy.
I would spend fifty five minutes defining the problem, and then I would need just five minutes to solve it.
The Leather Market
Weston Street
London, UK
SE1 3ER
+44 20 3743 7897
© Fifty Five and Five 2025 - Our head office is registered in England and Wales as company no. 07508740. VAT no. 107280831. Privacy policy.
I would spend fifty five minutes defining the problem, and then I would need just five minutes to solve it.
The Leather Market
Weston Street
London, UK
SE1 3ER
+44 20 3743 7897
© Fifty Five and Five 2025 - Our head office is registered in England and Wales as company no. 07508740. VAT no. 107280831. Privacy policy.
I would spend fifty five minutes defining the problem, and then I would need just five minutes to solve it.
The Leather Market
Weston Street
London, UK
SE1 3ER
+44 20 3743 7897
© Fifty Five and Five 2025 - Our head office is registered in England and Wales as company no. 07508740. VAT no. 107280831. Privacy policy.